Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
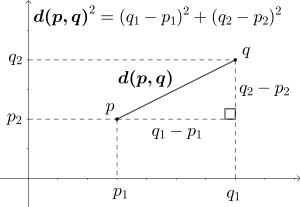
Selected image –

Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that the music of math rock band Jyocho has been alternatively described as akin to "madness" or "contemplative and melancholy"?
- ... that mathematician Daniel Larsen was the youngest contributor to the New York Times crossword puzzle?
- ... that after Archimedes first defined convex curves, mathematicians lost interest in their analysis until the 19th century, more than two millennia later?
- ... that although the problem of squaring the circle with compass and straightedge goes back to Greek mathematics, it was not proven impossible until 1882?
- ... that after Florida schools banned 54 mathematics books, Chaz Stevens petitioned that they also ban the Bible?
- ... that Fathimath Dheema Ali is the first Olympic qualifier from the Maldives?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that the word algebra is derived from an Arabic term for the surgical treatment of bonesetting?
More did you know –

- ...that the Electronic Frontier Foundation funds awards for the discovery of prime numbers beyond certain sizes?
- ...that pi can be computed using only the number 2 by the work of Viète?
- … that the Riemann Hypothesis, one of the Millennium Problems, depends on the asymptotic growth of the Mertens Function?
- … that every positive integer can be written as the sum of three palindromic numbers in every number system with base 5 or greater?
- … that the best known lower bound for the length of the smallest superpermutation was first posted anonymously to the internet imageboard 4chan?
- ...that the mathematician Grigori Perelman was offered a Fields Medal in 2006, in part for his proof of the Poincaré conjecture, which he declined?
- ...that a regular heptagon is the regular polygon with the fewest sides which is not constructible with a compass and straightedge?
Selected article –
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor (December 3, 1845, St. Petersburg, Russia – January 6, 1918, Halle, Germany) was a German mathematician who is best known as the creator of set theory. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence between sets, defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that the real numbers are "more numerous" than the natural numbers. In fact, Cantor's theorem implies the existence of an "infinity of infinities." He defined the cardinal and ordinal numbers, and their arithmetic. Cantor's work is of great philosophical interest, a fact of which he was well aware.
Cantor's work encountered resistance from mathematical contemporaries such as Leopold Kronecker and Henri Poincaré, and later from Hermann Weyl and L.E.J. Brouwer. Ludwig Wittgenstein raised philosophical objections. Nowadays, the vast majority of mathematicians who are neither constructivists nor finitists accept Cantor's work on transfinite sets and arithmetic, recognizing it as a major paradigm shift. (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus